Hearing loss is a condition that can develop gradually, often over the course of many years.
Often, the person affected does not realize a hearing loss exists until it begins to cause problems with how they communicate or a loved one urges them to seek help.
If a hearing loss is detected, early intervention will increase the likelihood of a positive outcome.
At the Audiology Clinic of Northern Alberta, we recommend a
hearing assessment every one to two years as part of your regular check-up. Your clinician will review your previous test results, medical history, noise exposure and conduct a communication assessment to determine if a problem with your hearing is developing. If you are bothered by tinnitus, our tinnitus assessment will provide additional information.
Hearing Loss is Common
Hearing loss is an issue many Canadians deal with on a daily basis.
- One out of every ten Canadians – of all ages – lives with some form of hearing loss.
- Hearing loss affects half of people over 65.
- 7 out of 10 people with a hearing loss are under the age of 60.
The team at the Audiology Clinic of Northern Alberta is dedicated to reducing the negative effects of hearing loss. We use our expertise to find the most appropriate technology and treatment options available to improve your quality of life, regardless of age.
Signs of Hearing Loss
- Asking for repetition.
- Missing key words in conversation and being forced to fill in the context.
- Difficulty hearing or understanding certain consonants.
- Hearing sound but not being able to make out what is being said.
- Speech sounds muffled.
- Need to turn up the television or radio.
- Missing alarms.
- Difficulty in the presence of background noise or in situations when more than one person is speaking.
- Starting to avoid social settings or events in fear of not hearing properly.
- Feeling strained after extensive listening.
- Increased reliance on lip reading for content.
- Experiencing ringing (tinnitus) in your ears.
- Experiencing tolerance issues with loud sounds.
- Localizing where sounds are coming from.
Causes of Hearing Loss
Aging
Natural aging of the auditory system (also referred to as presbycusis) is the most common type of sensorineural hearing loss. It occurs gradually and initially affects the ability to hear higher frequency (higher pitched) sounds.
Noise Exposure
Noise Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL) results from repetitive exposure to damaging noise (85 dB or louder) or extreme bursts of excessively loud noise (called acoustic trauma). It most commonly affects how you hear high-frequency sounds.
Genetics
Various forms of hearing loss can be hereditary or be caused by a genetic dysfunction of the auditory system.
Congenital
Hearing loss can result from experiences in the womb (resulting from exposure to drugs or alcohol, maternal diabetes, infections, preeclampsia, RH abnormalities or anoxia) or at birth (premature birth, low birth rate, severe jaundice, use of forceps or other extenuating circumstances).
Head Trauma and Concussions
Injury to the head can result in different types of hearing loss, including damage to the inner, outer or middle ear. It can also affect more than one part of the ear.
Medications
The side effects of certain medications have been known to affect the auditory system (usually the inner ear and auditory nerve). This has similar side effects to what is seen from chemical exposure.
Disorders of the Ear
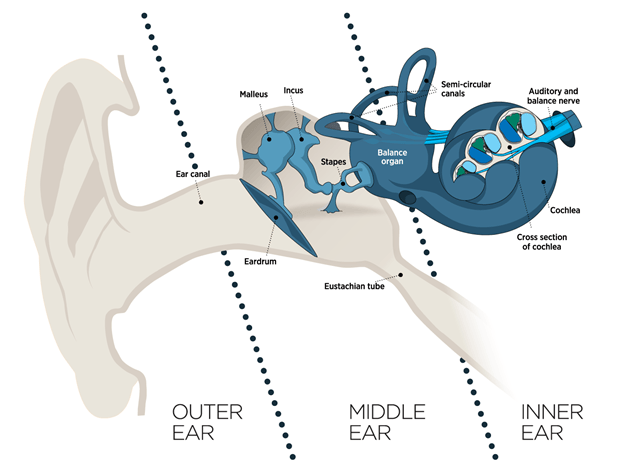
Outer ear
- Excessive wax
- Foreign objects
- Abnormal growths in the ear canal
- Malformation of the ear
- Infections
Middle ear
· Infections
· Eardrum perforation
· Eustachian tube dysfunction
· Otosclerosis
· Cholesteatoma
· Barotrauma
· Middle ear bone dysfunction
· Foreign objects
Inner ear and beyond
· Meniere’s disease
· Vestibular disorders
· Acoustic neuroma
· Autoimmune diseases
· Nerve disorders
Auditory processing disorders
Body disorders and diseases
· Meningitis
· Chickenpox
· Smallpox
· Severe fevers
· Shingles
· Viruses
· Anti-immune diseases
· Obesity
· Strokes,
· Disorders that affect the nervous system
· STD’s
· Hypertension and circulatory system disorders
· Smoking, drug use
Types of Hearing Loss
Not all hearing loss is the same. Many effective treatments have been designed to reduce the effects of the various forms of hearing loss.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss typically results from an inner ear dysfunction. If part of the inner ear is damaged, it is more difficult to transform mechanical energy into the electrical energy that is sent to the brain.
Sensorineural hearing loss can be the result of damage to the neural pathways or damage to the cochlea or hair cells. (“Sensory” refers to the cochlea and hair cells, while “neural” refers to the neural pathways.) It can be difficult to diagnose the type of damage in a traditional hearing test, so various types of inner-ear damage are grouped together.
Characteristic signs of sensorineural hearing loss
- Voices seem loud enough but are not clear
- Difficulties hearing sounds, especially soft sounds
- Difficulties distinguishing and differentiating among sounds, even loud sounds
- Low-level sounds are perceived to be far too soft, and high-level sounds are too loud
- Often accompanied by tinnitus
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss
- Aging
- Damage from noise
- Heredity or congenital
- Illness or medicine
- Acoustic neuroma (benign tumours near the auditory nerve)
- Strokes
Treatment
Hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or the nerve paths cannot be treated surgically or medically. Many people with sensorineural loss can, however, benefit from hearing aids. If the damage is too severe to benefit from hearing aids, cochlear implants are an option.
Conductive Hearing Loss
When sound is not conducted optimally through the outer or middle ear, the result is a conductive hearing loss. The specific hearing loss can originate in external ear, ear canal, eardrum, ossicles (middle ear bones) or a combination of these.
A conductive hearing impairment usually gives rise to mild to moderate hearing loss. The loss can affect all frequencies relatively uniformly or be especially pronounced in the low-frequency region.
- Causes of conductive hearing loss
- Ear wax completely blocking the ear canal
- Inflammation of the middle ear
- Perforation of the eardrum
- Otosclerosis
- Fracture in the chain of ossicles
- Deformity of the outer ear
Treatment
Most conductive hearing losses can be treated medically or surgically, such as when the hearing loss is caused by inflammation of the middle ear.
When surgical or medical intervention is not an option, people with conductive hearing loss can often be helped with hearing aids.
Mixed Hearing Loss
When a portion of the hearing loss is sensorineural and a portion is conductive, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss.
Treatment
Some mixed hearing losses may be medically or surgically treated, depending on the location or nature of damage.